Brute force attacks are a common form of cyber attack and can be carried out against a wide range of systems, including websites, databases, and network devices. Attackers can use automated tools to attempt different combinations of usernames and passwords until they find the correct one. The process can be time-consuming, but with the help of automated software, attackers can try thousands or even millions of combinations in a short period.
Fail2ban is a versatile tool that can be used to protect a wide range of services, including SSH, FTP, and web servers. The software is free, open-source, and has a wide user community that provides support and updates. Fail2ban is available for most operating systems and is relatively easy to install and configure, even for novice users.
SSH and FTP are two commonly used protocols that are vulnerable to brute force attacks. In the case of SSH, the attacker tries to guess the correct username and password combination to gain access to a remote server. Once they gain access, the attacker can carry out a variety of malicious activities, including stealing data, installing malware, or disrupting services.
FTP brute force attacks involve guessing the correct login credentials for a specific FTP server to gain access to the files stored on that server. The attacker can then download, modify, or delete files as they see fit.
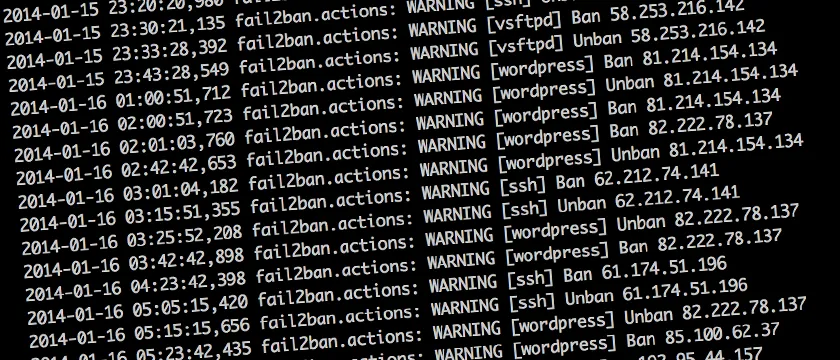
Fail2ban is a useful tool for preventing brute force attacks against SSH and other services. The tool works by monitoring log files for suspicious activity and blocking IP addresses that exhibit such behavior. When an attacker attempts to log in to a protected service and fails a certain number of times within a specified period, fail2ban automatically blocks the IP address used by the attacker.
Installing fail2ban is a straightforward process that varies depending on the operating system you are using. For instance, on a Debian-based Linux system, you can install fail2ban using the following command:
sudo apt-get install fail2ban
The default settings for fail2ban are usually sufficient for most users, but it is recommended to configure the tool to suit your specific needs. For example, you can adjust the number of failed login attempts that trigger a ban or set up email notifications to alert you when an attack is detected.
Once installed, fail2ban needs to be configured to monitor the log files of the services you wish to protect. In the case of SSH brute force attacks, the configuration file for SSH is located in the /etc/fail2ban/jail.d/ssh.conf file. To enable SSH protection, you need to edit this file and set the enabled parameter to true. You can also configure other parameters such as the maximum number of login attempts and the duration of the ban.
Fail2ban works by analyzing log files for failed login attempts and triggering an action when a predefined threshold is reached. The action can be to block the IP address of the attacker or to send an email notification to the system administrator. Once an IP address is blocked, the attacker will not be able to establish a connection to the system, making it more difficult to carry out a successful attack.
In summary, a brute force attack is a type of cyber attack where an attacker tries different combinations of usernames and passwords to gain unauthorized access to a system. SSH and FTP are common targets of brute force attacks, but fail2ban can be used to prevent such attacks by blocking suspicious IP addresses. Fail2ban is a versatile tool that is free, open-source, and easy to use, making it an ideal choice for protecting your system against brute force attacks.